Data Exchange Service
The data exchange service is a separate module to formalize data handling in terms of logging and locking.
Add backend components
In order to deploy the model and services from the framework to your project, you have to import them both. To do so, add the following two packages including their content into their respective paths.
1from valuea_framework.model.valuea.des import *
1import valuea_framework.services.valuea.des
2import pkgutil
3__path__ = pkgutil.extend_path(valuea_framework.services.valuea.des.__path__,
4 valuea_framework.services.valuea.des.__name__)
The first one makes sort deploymodel --rdbms will known which tables to create, the other one imports
our standard services into the valuea.des namespace.
Management user interface
Part of the framework is a standard module which utilizes the services installed earlier for management purposes, when this module is installed you can easily inspect the jobs started by the system and disable future executions if needed.
To install, use the following command on a frontend server:
pkg add -f os-valuea-des-x.y.txz
usage
The basic concept of DES is to facilitate a standard import workflow for files and messages, which in many cases should be handled as a singleton operation. DES relies on a model and uses standard database locking to assure consistency among difference processes.
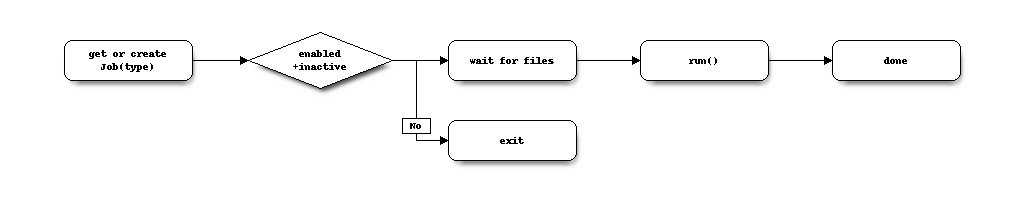
Imagine a set files needs to be processed, but only when they are in a consistent state on disk and we need to assure that another process trying to do the same won’t start in the same timeframe. Our process might look as follows.
We first would register our task which identifies our job, then check if we are ready to run, if so wait for the files to complete , run our import action (whatever it looks like) and close our process.
In code, without the actual import with logging included this would looks as follows (__file__ is the script itself).
1import valuea_framework.des
2
3desjob = valuea_framework.des.DESJob('XXX')
4if desjob.lock() and desjob.is_enabled():
5 desjob.create_instance()
6 desjob.log('wait for files', log_type="INFO", flush=True)
7 valuea_framework.des.wait_for_files([__file__])
8 desjob.log('start import', log_type="INFO", flush=True)
9 desjob.log('do run() action', log_type="INFO", flush=True)
10 desjob.close_instance(u'PCD')
11 # desjob.disable()
12 desjob.unlock()
The log information can be examined using the management console installed in the previous chapter.